Within project management processes, the identification of resources represents a crucial phase for the correct setup and management of the project. A well-structured plan, in fact, cannot be limited to defining objectives, costs, and timelines, but must precisely identify the necessary resources—human, technical, material, and financial—ensuring they are available, adequate, and properly allocated.
This activity assumes a strategic value because it directly influences the effectiveness of subsequent phases of planning, scheduling, control, and monitoring. A superficial or incomplete assessment of resources can generate imbalances, inefficiencies, and issues that affect the timing, quality, and sustainability of the intervention.
The identification of resources, therefore, is not merely an inventory exercise, but a methodical and interdisciplinary process that aims to align project needs with actual availability, optimizing the use of means and skills throughout the entire project lifecycle.

The resource analysis must systematically cover all components necessary to achieve the objectives:
The most significant component concerns professional skills and operational teams. It is necessary to identify:
Proper mapping allows for the avoidance of critical skill shortages and the definition of an organizational chart consistent with the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS).
These include construction materials, plant components, technological supplies, and equipment. Identification must consider:
The role of support technologies for design, management, and implementation is increasingly significant. Among these:
The economic component is transversal and concerns the availability of capital, credit lines, public contributions, or structural funds. Identifying expected financial flows is essential for cash flow planning and avoiding liquidity imbalances.


Resource identification utilizes standardized methodologies and established technical tools:
Resource identification cannot be considered an isolated activity but must integrate with the entire planning process. In particular:
In this way, consistency between the technical, economic, and temporal dimensions of the project is ensured.
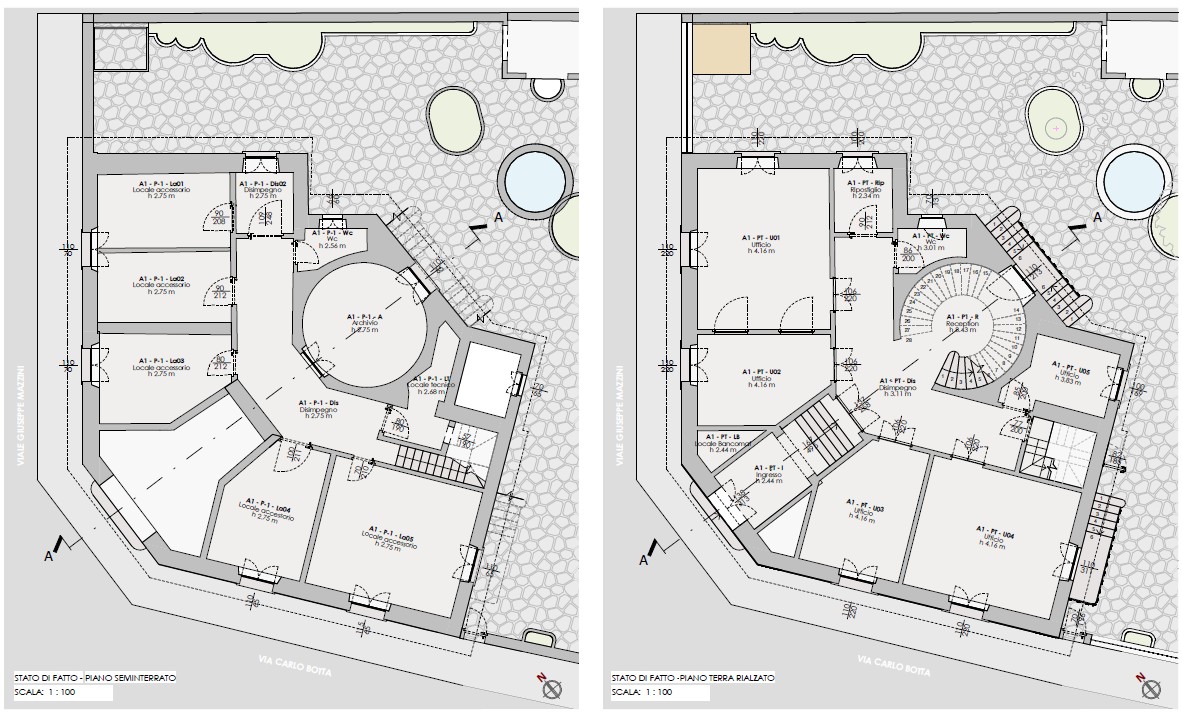
The increasing complexity of projects requires advanced digital tools for effective resource management:
A systematically conducted resource identification process brings tangible benefits:


Resource identification constitutes one of the most strategic activities of integrated project management. It allows for the transformation of general objectives into a sustainable operating system, ensuring that means, skills, and capital are available and adequately utilized.
Accurate resource management based on technical methodologies reduces risks, improves efficiency, and ensures consistency between planning and implementation.
In a context where projects are increasingly complex and multidisciplinary, accurate resource identification becomes a critical success factor, capable of ensuring not only feasibility but also quality and sustainability of the intervention.