In the construction sector, characterized by increasing project complexity and a more multidisciplinary approach, project reports and technical manuals play a central role in ensuring clarity, traceability, and consistency across the different phases of the construction process. These are not merely descriptive documents, but operational tools that allow for the unambiguous communication of technical information, performance specifications, construction methodologies, and management procedures for the work.
In the context of detailed executive design, the drafting of reports and manuals is essential: on one hand, it allows for the documentation and validation of design choices, and on the other, it provides a practical guide for construction, testing, maintenance, and use of the building. A project lacking complete and structured documentation risks generating ambiguities, execution errors, and difficulties in future management.
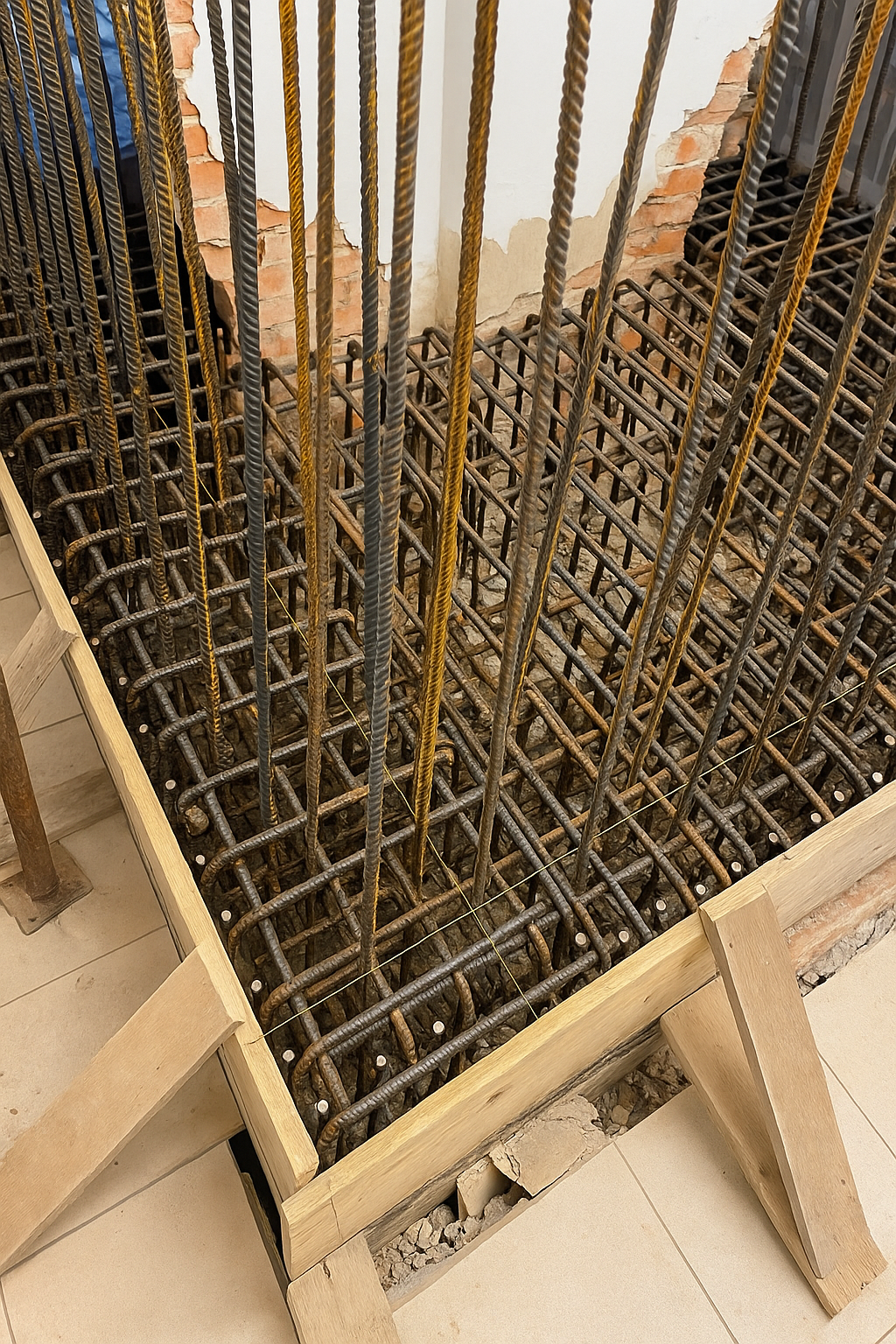
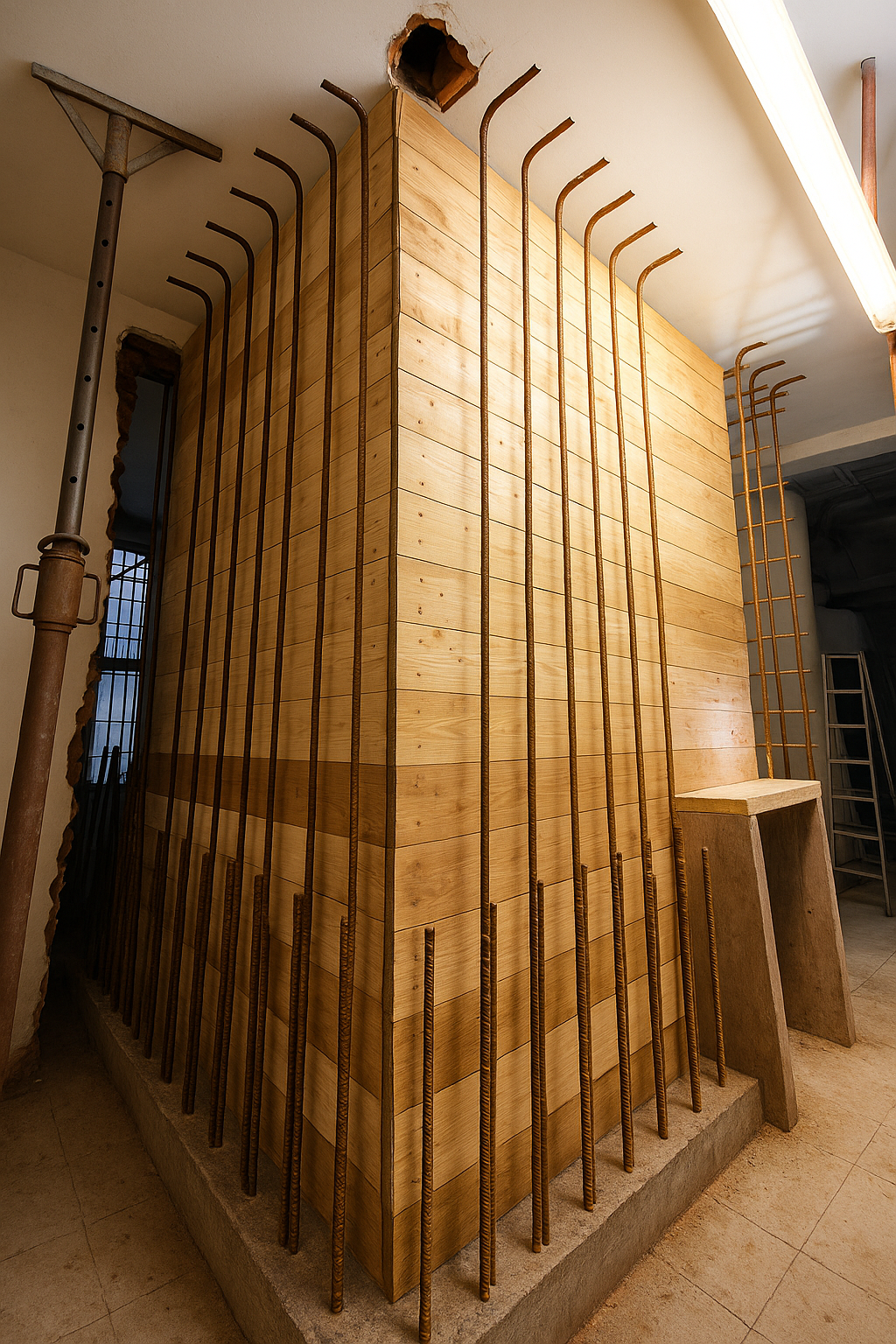


Project reports and technical manuals accompany the entire lifecycle of the work:
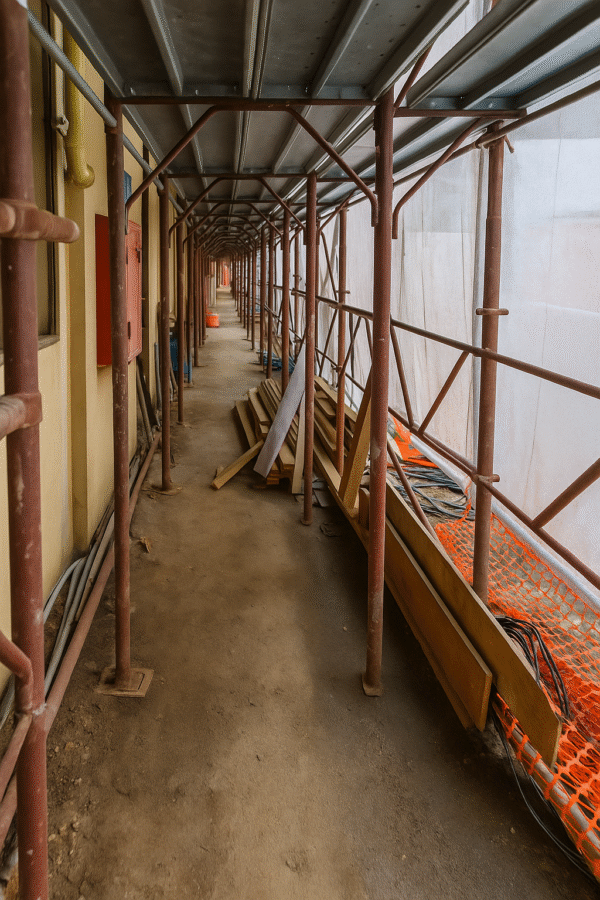

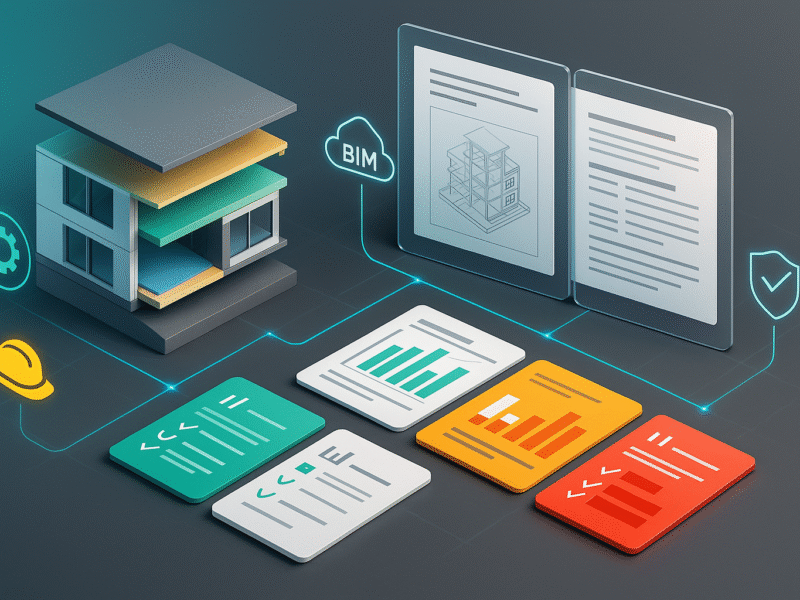
Project reports and technical manuals are essential tools in detailed executive design. They are not mere accessory documents, but an integral part of the construction process: the former ensures traceability and validation of design choices, while the latter provides operational guidelines for installation, use, and maintenance.
From a modern perspective, based on digitalization and sustainability, the quality of technical documentation is directly proportional to the quality of the built environment and its ability to maintain performance over time. Investing in the accurate drafting of reports and manuals therefore means investing in the durability, efficiency, and enhancement of the work.