The construction sector, historically one of the most energy-intensive and environmentally impactful, is now called to undergo a profound transformation to address the challenges of climate change, the scarcity of natural resources, and new sustainability regulations. In this context, environmental technologies play a strategic role: they allow for the reduction of emissions, optimization of resource use, improvement of living comfort, and enhancement of building resilience to extreme weather events.
These are no longer marginal or niche solutions, but essential tools to be integrated into the design, construction, and management processes. The adoption of environmental technologies enables us to rethink construction as an intelligent and interconnected system, capable of ensuring efficiency, quality, and sustainability throughout the entire lifecycle of the project.
Environmental technologies find application in various areas of construction, each with a significant impact on the overall sustainability of the built environment.

Environmental technologies in construction integrate with advanced analysis and evaluation methodologies:
The integration of environmental technologies in the construction sector generates tangible benefits on multiple levels:
Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, improvement of air quality, mitigation of heat island effects.
Reduction of operational costs due to energy and water efficiency, increased material longevity, and reduced maintenance expenses.
Improvement of living comfort, health, and safety for occupants.
Enhancement of real estate value and increased market competitiveness.
Compliance with European and national directives on sustainability, efficiency, and resilience.
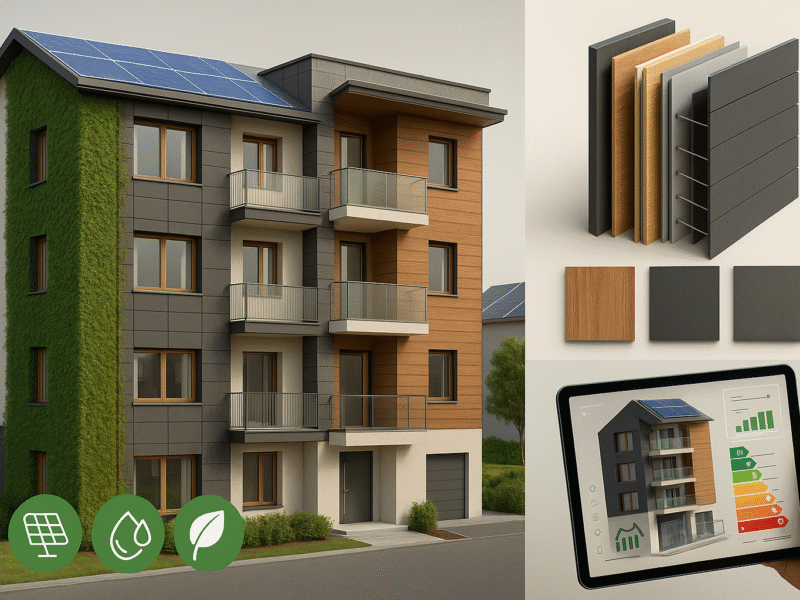


Environmental technologies today constitute an essential pillar for the construction sector. Their application not only reduces environmental impacts but also improves building performance, generates economic and social value, and ensures resilience to climate challenges.
The future of construction will increasingly be characterized by the integration of sustainable technological solutions, capable of transforming the built environment into an intelligent, circular, and efficient system. Investing in environmental technologies means building not only “greener” buildings and cities but also more resilient, functional, and oriented towards the well-being of people and communities.